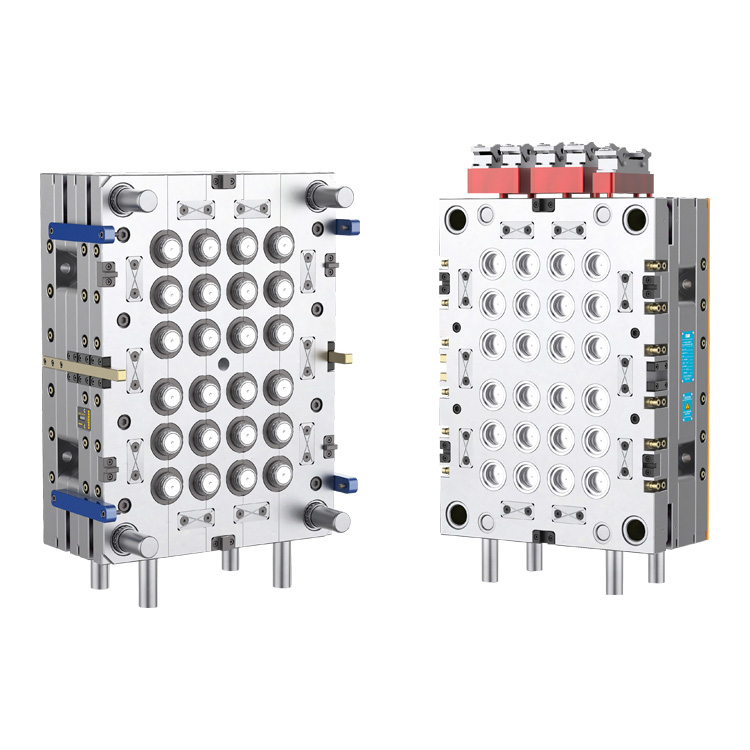
Gateway to Precision: Considerations for Gate Design in a 24-Cavity Cap Mold
2024-01-17
Introduction:
In the realm of injection molding, the gate serves as the gateway through which molten material flows into the mold cavity. The design of the gate in a 24-cavity cap mold is a critical element that significantly influences the overall efficiency, quality, and waste reduction in the molding process. This blog delves into the specific considerations for gate design to achieve optimal filling and minimize waste in the production of 38mm caps.
1. Gate Location and Distribution:
The strategic placement of gates within a 24-cavity cap mold is crucial for achieving optimal filling. Engineers carefully select gate locations to ensure uniform material distribution across all cavities, minimizing variations in cap dimensions and reducing the risk of defects.
2. Balanced Gate Sizing:
Achieving a balance in gate sizes is essential for uniform filling. In a 24-cavity mold, each gate must be designed with consistent dimensions to prevent variations in injection pressure and material flow. This balance contributes to the overall quality and consistency of molded caps.
3. Optimal Gate Size for Material Flow:
The size of the gate is directly related to the material's flow characteristics. The gate size is carefully selected to facilitate smooth material flow into the mold cavities, preventing issues such as incomplete filling, short shots, or excess waste due to overfilling.
4. Gate Type:
Various gate types, such as sprue gates, edge gates, or hot runner gates, may be considered based on the specific requirements of the cap design and molding process. Each gate type has unique advantages and considerations related to material flow, pressure, and waste reduction.
5. Hot Runner Systems:
Hot runner systems are often employed in 24-cavity cap molds to eliminate the need for runners and reduce material wastage. The design of hot runner gates ensures precise control over material flow and temperature, contributing to efficient filling and reduced waste.
6. Runnerless Molding Technology:
Runnerless molding technology eliminates the need for traditional runners entirely. This innovative approach minimizes waste by directly injecting material into each cavity without the use of runners, optimizing material usage and reducing environmental impact.
7. Gate Vestige Management:
Gate vestige, the small remnant of material left at the gate location, is carefully managed in the design process. Engineers consider gate vestige size and placement to ensure it does not interfere with the functionality or aesthetics of the final caps, reducing the need for additional finishing processes.
8. Gate Freeze-Off Control:
Gate freeze-off, the solidification of material at the gate during cooling, is managed through precise temperature control. The gate design incorporates features to minimize freeze-off, ensuring continuous material flow and reducing the risk of defects in the molded caps.
9. Gate Rheology Analysis:
Advanced simulations and rheology analyses are conducted during the design phase to model material flow through the gate. This analysis helps optimize gate design for the specific characteristics of the molding material, contributing to efficient filling and waste reduction.
10. Gate Quality Control Measures:
Incorporating quality control measures, such as sensors or monitoring systems, during the production process allows for real-time detection of variations in gate performance. Early identification of issues ensures prompt adjustments to maintain optimal filling and reduce waste.
Conclusion:
The gate design in a 24-cavity cap mold is a meticulous process that requires a balance between optimal filling, waste reduction, and quality control. By considering factors such as gate location, size, type, and innovative technologies like hot runners or runnerless molding, engineers strive to achieve precision in material distribution. As the injection molding industry continues to evolve, the ongoing refinement of gate designs remains pivotal in achieving efficiency, sustainability, and high-quality standards in cap production.